Requirements specifies the functionality of a system.
Once requirements are written, methods for ensuring that the system contains the functionality specified must be developed. There are a number of methods for validating functionality and determining if the system reacts in the expected way: requirements testing, inspections, analysis, and demonstrations.
To validate the requirements, test plans are written that contain multiple test cases; each test case is based on one system state and tests some functions that is based on a related set of requirements.
In the total set of test cases, each requirement must be tested at least once, and some requirements will be tested several times because they are involved in multiple systems in varying scenarios and in different ways.
A system measurement methodology is a systematic method of measuring, assessing, and adjusting the system development process using objective data, used to assess progress, quality, and performance throughout the development. In this context:
– Measures are the numbers used to create the metrics
– Metrics are the numbers turned into information
Metrics shall be used to define targets and to monitor progress against those targets.
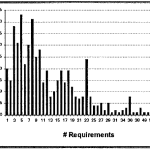
An example of metric for requirements testing characterizes the test plan and identify any lack or excess of testing.
Since each test costs money and takes time, the obvious questions are how may requirements are covered by one test, and how many tests cover only one requirement. On the other hand, if requirements are insufficiently tested, a corrective strategy must be followed. The chart below shows an exceed of test for requirements 3,5,8 and identifies risks on many requirements from 30 to 62.
Did you like this post? Would you like to be informed about the last railway signalling technical and commercial news? Join us on LinkedIn and stay updated!
railwaysignalling.eu | walk the rail talk