Railway maintenance is one of the most challenging tasks to be carried out by all the railway infrastructure managers worldwide located, because of the high effort required in terms of time and costs.
A railway service or asset needs to be highly reliable, therefore the equipment must be kept in good working conditions and regular railway maintenance is essential in order to achieve this goal.
For these reasons, innovative maintenance solutions for railway systems, as well as integration of maintenance into operation, are costantly studied and developed in order to ensure a better management of the railways and rolling stocks.
Railway maintenance is defined as the process of preserving a condition or the state of being preserved, along the track or related to vehicles, but there are actually different approach to mantain a railway asset or service:
1. Corrective Railway Maintenance
It is a task performed to identify, isolate and resolve a fault so that a failed equipment can be replaced or restored to an operational condition within the tolerances or limits established for in-service operations. With this approach, no actions are taken in order to prevent a fault, since the only way to detect it is waiting for an equipment to fail.
2. Preventive Railway Maintenance
It is a task regurarly performed to monitor the status or the conditions of a railway equipment, in order to lessen the likelihood of its fail. An approach like this allows the infrastructure managers to recognise a bad health of an asset, thefore a preventive action can be taken before a fail, ensuring a better reliability of the whole system.
3. Predictive Railway Maintenance
Predictive maintenance techniques are designed to help determine the condition of in-service equipment in order to predict when it is going to fail, therefore it is not a matter of likelihood, but a highly detailed forecast is ensured. This approach promises cost savings over routine or time-based, because tasks are performed only when warranted.
The most modern approaches to engineering maintenance, applicable to the railway, as well as any complex system, are well described in this book.
Did you like this post? Would you like to be informed about the last railway signalling technical and commercial news? Join us on LinkedIn and stay updated!
railwaysignalling.eu | walk the rail talk



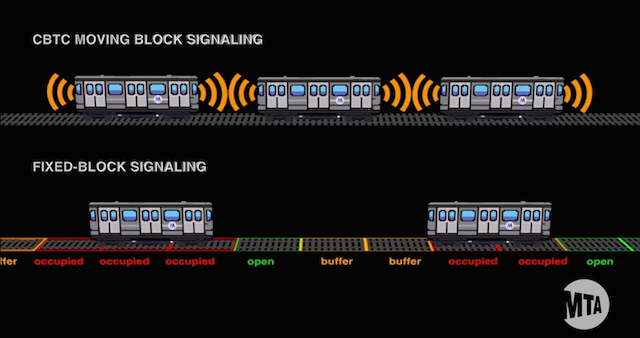


Implementing a comprehensive approach to maintenance, encompassing corrective, preventive, and predictive strategies, is essential for ensuring the reliability, safety, and efficiency of railway applications. By proactively identifying and addressing potential issues through preventive and predictive measures, railway operators can minimize downtime, optimize maintenance schedules, and maximize the lifespan of critical assets.